Oceanologia No. 40 (3) / 98
Contents
Papers
Dissertations
Papers
Finding the aerosol optical thickness over the Baltic Sea – comparison of two methods
Oceanologia 1998, no. 40 (3), pp. 165–182
Anna Rozwadowska, Jolanta Kuśmierczyk-Michulec
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences,
Powstancow Warszawy 55, 81–712 Sopot, Poland; ania@iopan.gda.pl
Keywords: Aerosol optical thickness, Retrieval methods, Baltic atmosphere
Manuscript received June 29, 1998, in final form July 30, 1998
Abstract
The results of two methods used to estimate the aerosol optical
thickness over the Baltic Sea are compared. The standard method
is based on measurements of the direct component of the
downward irradiance at the sea surface in 8 spectral bands
(412, 443, 490, 510, 555, 670, 765, 865 nm – the same as
SeaWiFS). In the pyranometric method, Baltic aerosols are
assumed to be a mixture of model aerosol types with strictly
defined optical properties, i.e. maritime, continental and
stratospheric types. Their proportion in the Baltic aerosol is
found from broadband spectral downward irradiance measurements
(VIS, IR) using the radiative transfer model. Simultaneous
measurements of the spectral downward irradiance and its direct
component on cloudless days in the southern Baltic were used in
the comparison. The pyranometric method of estimating the
aerosol optical thickness proved to be a satisfactory tool.
Depending on the wavelength, the statistical errors in it are
not in excess of 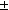 0.06 to
0.06 to 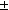 0.08.
0.08.
Inter-annual oscillations of Baltic water volumes and sea levels:
Oceanologia 1998, no 40 (3), pp. 183–203
Andrzej Wróblewski
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Powstancow Warszawy 55, 81–712 Sopot, Poland; wroblew@iopan.gda.pl
Keywords: Baltic volume, Long-term oscillations, Sea level
Manuscript received July 2, 1998, in final form August 28,
1998.
Abstract
In spite of the existence of recent long-term sea level measurement series, these have not been applied to
compute the long-term characteristics of Baltic water volume changes. To
deal with the problem, the mean annual volume changes in the Baltic basin
were computed for the measurement period 1896–1986 on the basis of mean
monthly sea levels at six tide gauges. EOFs were applied to obtain the
averaged sea level characteristics for the entire basin. The results
were compared with those of calculations based on the readings of the
Stockholm tide gauge, regarded as representative of the whole Baltic, and
on geodetic measurements. The differences were found to be minimal.
Following computation of the mean annual water volumes, the time series
obtained was subjected to a Finite Fourier Transform. The resulting
amplitude spectrum was worked up with the bootstrap technique at the 5%
significance level, yielding oscillations with periods of 5.6,
4.5 and 3.6 years and corresponding volume change amplitudes
of 7.9, 8.7 and 8.7 km3. The fundamental statistical
characteristics of the Baltic water volume changes were
determined together with the application of stochastic parametric
processes. A forcing study of the long-term water volume
oscillations in the Baltic is included.
Maximum-entropy probability distribution of wind wave
free-surface elevation
Oceanologia 1998, no 40 (3), pp. 205–229
Witold Cieślikiewicz
Institute of Hydro-Engineering, Polish Academy of Sciences, Kościerska 7, 80–953 Gdańsk, Poland; witold_c@bryza.ibwpan.gda.pl
Keywords: Maximum-entropy principle, Maximum-entropy probability distribution,
Random water waves, Wind waves, Free-surface elevations
Manuscript received June 16, 1998, in final form July 23,
1998.
Abstract
The probability density function of the surface elevation of a non-Gaussian
random wave field is obtained. The derivation
is based on the maximum entropy (information)
principle with the first four statistical moments of the surface elevation
used as constraints. The density function is found by the use of the
Lagrangian multipliers method and it is shown that only two of four
Lagrangian
multipliers are independent.
The applied method of numerical solution is described in detail
and the useful
nomograms that give the Lagrangian multipliers as functions of skewness and
kurtosis are calculated and incorporated in the paper.
For slightly nonlinear waves the approximate maximum-entropy probability
distribution is developed. The condition of the existence of this
approximate
distribution agrees with the empirical criterion for small deviations from
the Gaussian distribution of random water waves.
The theoretical results compare well with field experiment data of
Ochi and Wang (1984), even in the strongly non-Gaussian case.
Energy value of the mud crab Rhithropanopeus harrisii ssp.
tridentatus (Crustacea, Decapoda) in relation to season, sex and size
Oceanologia 1998, no 40 (3), pp. 231–241
Anna Wiszniewska, Agata Rychter, Anna Szaniawska
Institute of Oceanography, Gdańsk University, Al. Marszalka J. Pilsudskiego 46, 81–378 Gdynia, Poland; oceasz@univ.gda.pl
Keywords: Crustacea, R. harrisii tridentatus, Energy value, Vistula Lagoon
Manuscript received June 10, 1998, in final form August 7, 1998.
Abstract
The energy value of male and
female Rhithropanopeus harrisii tridentatus of various carapace
width classes was determined. Crab samples were collected in the Vistula
Lagoon from April to November 1995. The population of R. harrisii
tridentatus from the Vistula Lagoon was characterised by a very low energy
value
7.97 [SD] 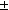 1.5 J mg-1DW, (12.69 [SD]
1.5 J mg-1DW, (12.69 [SD] 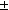 2.1 J mg-1 AFDW). The average amount of ash in this population
was 37.66% of dry weight (organic matter was 62.44%). In each month
(except September) the calorific value of the females exceeded that of the males;
this value also varied seasonally. The calorific value of the population dropped
to a minimum in August, whereas the maximum level was recorded in September.
2.1 J mg-1 AFDW). The average amount of ash in this population
was 37.66% of dry weight (organic matter was 62.44%). In each month
(except September) the calorific value of the females exceeded that of the males;
this value also varied seasonally. The calorific value of the population dropped
to a minimum in August, whereas the maximum level was recorded in September.
Meiobenthic communities of the Pomeranian Bay (southern Baltic):
effects of proximity to river discharge
Oceanologia 1998, no 40 (3), pp. 243–260
Joanna Rokicka-Praxmajer, Teresa Radziejewska, Halina Dworczak
Department of Oceanography, Agricultural University, Kazimierza Krolewicza 4, 71–550 Szczecin, Poland; tr@iom.gov.pl
Keywords: Meiobenthos, Baltic Sea, Estuary, River discharge, Organic enrichment
Manuscript received April 29, 1998, in final form July 13, 1998.
Abstract
The Pomeranian Bay (southern Baltic Sea) is a component
of the river Oder (Odra) estuarine system. It receives the Oder's discharge
once it has passed through the Szczecin Lagoon, a eutrophic and polluted
water body. The discharge has been documented as affecting the hydrography
of the pelagic domain as well as the sedimentary environments and the
macrozoobenthos of the Bay. This study focused on the
distribution of meiobenthic communities in the Bay as investigated
with the use of a suite of uni- and multivariate analyses applied to data
collected at 14 stations in September 1993. Meiobenthic community
characteristics (composition and abundance) are presented in relation to
sediment properties (grain size, silt/clay and organic matter
content), changing with distance from the major riverine discharge site.
The communities studied showed a clear distinction between those associated
with organic matter-enriched sediments close to the discharge site and the
assemblages living in clean sands, away from the discharge. We conclude
that the meiobenthos can be regarded as another compartment of the Pomeranian
Bay system responding to the River Oder discharge.
The hydrological and hydrochemical division of the surface
waters in the Gulf of Gdańsk
Oceanologia 1998, no 40 (3), pp. 261–272
Jacek Nowacki
Institute of Oceanography, Gdańsk University, Al. J. Pilsudskiego 46, 81–378 Gdynia, Poland; ocejn@univ.gda.pl
Ewa Jarosz
Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA 70803, USA
Keywords: Gulf of Gdańsk, Surface water, Temperature, Salinity, Nutrients,
Surface layer division, Cluster analysis, Ward's method
Manuscript received May 8, 1998, in final form July 15, 1998.
Abstract
The objective of this work was to define regions in the surface
layer of the Gulf of Gdańsk that are characterised by different natural
(temperature, salinity, total water
depth) and anthropogenic (concentrations of major nutrients) factors.
Additionally, approximate boundaries between the regions distinguished
were delineated. To find regions of different hydrological and hydrochemical
properties, Ward's method, an agglomerative hierarchical cluster technique,
was applied to a data set containing measurements of temperature, salinity,
total depths and nutrient concentrations.
Cluster analysis divided the surface waters of the Gulf of Gdańsk
into seven regions. The surface waters in the shallow water part of the
Gulf of Gdańsk, where six out of the seven regions were located,
displayed a distinct diversity which was probably associated with the
morphometry of the Gulf, nutrient sources and freshwater input. The
last region encompassed the deep-water part of the Gulf of Gdańsk and Puck Bay.
Dissertations
Transfrontal exchange of mass and heat in the region of the Arctic front
(review by Jerzy Cyberski)
Oceanologia 1998, no 40 (3), pp. 273–275
Waldemar Walczowski
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Powstancow Warszawy 55, 81–712 Sopot, Poland; walczows@iopan.gda.pl
Ph. D. thesis in physical oceanography supervised by Professor Jan Piechura