Oceanologia No. 39 (2) / 97
Contents
Papers
- Sławomir Kaczmarek, Olga J. Koblentz-Mishke, Stanisław Ochocki, Jan Nakonieczny, Henryk Renk:
Primary production in the eastern and southern Baltic Sea
- Dorota Napierska, Marie T. Thebault, Janusz Pempkowiak, Edward Skorkowski:
Comparison of short-term cadmium poisoning in the shrimp Crangon crangon from the Baltic Sea and the shrimp Palaemon serratus from the Atlantic Ocean with cadmium bioaccumulation and malic
enzyme activity in abdomen muscle
- Joanna Kożuch, Iwona Wilkowska, Janusz Pempkowiak:
The kinetics of cadmium accumulation and loss from Mytilus trossulus
in the presence of marine humic substances
- Joanna Kożuch, Janusz Pempkowiak, Gotfryd Kupryszewski, Piotr Mucha,
Piotr Rekowski, Joanna Smol:
Analysis of ferritin-type proteins in the hepatopancreas of Baltic
blue mussel (Mytilus trossulus)
- Sergey I. Pogosyan, Marina A. Sivchenko, Viktor N. Maximov,
Mirosława Ostrowska:
Physiological heterogeneity of an algal population: classification of
Scenedesmus quadricauda cenobia by the features of their
photosynthetic apparatus
- Justyna Miac, Malgorzata Groth, Maciej Wolowicz:
Seasonal changes in the Mya arenaria (L.) population
from Inner Puck Bay
Chronicle
Prof. Krystyna Wiktor (Obituary) by Marcin Plinski
Oceanologia
1997, no. 39 (2), pp. 113-116
Papers
Sławomir Kaczmarek
Institute
of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Olga J. Koblentz-Mishke
Shirshov Institute of Oceanology, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow
Stanisław Ochocki, Jan Nakonieczny, Henryk Renk
Sea Fisheries Institute, Gdynia
Primary production in the eastern and southern Baltic Sea
Oceanologia
1997, no. 39 (2), pp. 117-135
Keywords: Primary production; Spatial distribution; Baltic Sea
Manuscript received April 29, 1997, in final form June 3, 1997.
Abstract
The results of long-term measurements of the
photosynthetic primary production in the Baltic Sea have been
collected (over 800 daily values from the 1968-1991). During
this period substantial eutrophication of the sea was found to
have taken place, leading to an annual increase in production
of between 5.2 and 10 g C m-2
in consecutive years, depending
on the area. Taking this process into account, a map of annual
production in 1991 was prepared. This shows the production in
the sea to be spatially highly diverse, a fact which can
probably be explained by the influence of the dynamics of
nutrient-carrying water masses.
Dorota Napierska
Biological Station, Gdańsk University, Gdańsk-Sobieszewo
Marie T. Thebault
Laboratoire de Biologie Marine, College de France, Concarneau, France
Janusz Pempkowiak
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Edward Skorkowski
Marine Biology Centre, Polish Academy of Sciences, Gdynia
Comparison of short-term cadmium poisoning in the shrimp
Crangon crangon from the Baltic Sea and the shrimp Palaemon serratus from the Atlantic Ocean with cadmium bioaccumulation and malic enzyme activity in abdomen muscle
Oceanologia
1997, no. 39 (2), pp. 137-146
Keywords: Cadmium poisoning; Shrimp; C. crangon; P. serratus; Abdomen muscle; Malic enzyme
Manuscript received January 22, 1997, in final form March 17, 1997.
Abstract
Shrimps were exposed to various concentrations of
CdCl2
under laboratory conditions for 96 h. Although kept at the same
Cd2+
concentration but at different salinities - C. crangon in
Baltic seawater (6 PSU) and P. serratus in Atlantic water
(36 PSU) - the shrimps accumulated a
Cd2+
level in abdomen muscle which was much higher in the animals kept
at the lower salinities than in those at the higher ones.
The same
Cd2+
bioaccumulation of ca 80 ng g-1
w.w. of abdomen muscle were found in C. crangon kept in 0.2 mg dm-3 of CdCl2
in
Baltic seawater and in P. serratus kept in 2 mg dm-3 of CdCl2 in Atlantic water. In both cases the NADP-dependent malic enzyme activity per
g w.w. of shrimp abdomen muscle was higher by ca 150% in animals kept at a CdCl2
concentration close to LC50
as compared to the control
groups.
Joanna Kożuch, Iwona Wilkowska, Janusz Pempkowiak
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
The kinetics of cadmium accumulation and loss from Mytilus trossulus
in the presence of marine humic substances
Oceanologia
1997, no. 39 (2), pp. 147-156
Keywords: Mytilus trossulus; Cadmium; Radiotracer; Accumulation;
Depuration; Humic substances; Temperature
Manuscript received February 28, 1997, in final form April 4, 1997.
Abstract
The accumulation and loss of cadmium (Cd) by the Baltic blue mussel Mytilus trossulus in the presence of marine humic substances (HS) was
investigated under laboratory conditions. The organisms were exposed to Baltic
Sea water (salinity 7.0 PSU, pH 7.9) containing cadmium (50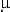 g Cd dm-3)
or radiocadmium (9 kBq 115mCd dm-3) and humic substances (0.0-7.2 mg HS dm-3).
Experiments were carried out in seawater at two different constant
temperatures (6oC
g Cd dm-3)
or radiocadmium (9 kBq 115mCd dm-3) and humic substances (0.0-7.2 mg HS dm-3).
Experiments were carried out in seawater at two different constant
temperatures (6oC  1oC or 15oC
1oC or 15oC  1oC).
The exposure time ranged from 8 to 21 days.
It was found that marine humic substances stimulate cadmium accumulation
by the mussels; however, the effect was strongly modified
by temperature. At 6oC
cadmium was preferably accumulated in the gills while at 15oC
the metal was stored mainly in the hepatopancreas. Two pools
of cadmium accumulated by Mytilus trossulus were detected.
Cadmium adsorbed to the shell was desorbed quickly and efficiently after the
mussels, previously grown in seawater containing an elevated metal concentration
(8 days, 50
1oC).
The exposure time ranged from 8 to 21 days.
It was found that marine humic substances stimulate cadmium accumulation
by the mussels; however, the effect was strongly modified
by temperature. At 6oC
cadmium was preferably accumulated in the gills while at 15oC
the metal was stored mainly in the hepatopancreas. Two pools
of cadmium accumulated by Mytilus trossulus were detected.
Cadmium adsorbed to the shell was desorbed quickly and efficiently after the
mussels, previously grown in seawater containing an elevated metal concentration
(8 days, 50 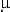 g Cd dm-3 or 9 kBq 115m Cd dm-3),
had been transferred to natural seawater (60 days, 0.03
g Cd dm-3 or 9 kBq 115m Cd dm-3),
had been transferred to natural seawater (60 days, 0.03 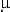 g Cd dm-3, 0 kBq 115m Cd dm-3).
The other pool of cadmium, accumulated in
the soft tissue of the mussels, remained intact after depuration
experiments lasting several weeks. Humic substances had no
effect on the depuration of cadmium from either pool.
g Cd dm-3, 0 kBq 115m Cd dm-3).
The other pool of cadmium, accumulated in
the soft tissue of the mussels, remained intact after depuration
experiments lasting several weeks. Humic substances had no
effect on the depuration of cadmium from either pool.
Joanna Kożuch, Janusz Pempkowiak, Gotfryd Kupryszewski
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot,
Piotr Mucha, Piotr Rekowski
Department of Bioorganic Chemistry, Faculty of Chemistry, Gdańsk University, Gdańsk
Joanna Smol
Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry, Polish Academy of Sciences, Poznan
Analysis of ferritin-type proteins in the hepatopancreas of Baltic blue mussel (Mytilus trossulus)
Oceanologia
1997, no. 39 (2), pp. 157-162
Keywords: Mytilus trossulus; Ferritin; Capillary electrophoresis
Manuscript received May 13, 1997, in final form June 20, 1997.
Abstract
Ferritin is a protein able to store and transport not only iron, but also,
though to a lesser extent, some other heavy metals, including cadmium. This
study concerned the analysis of ferritin-type proteins in a dominant species
of the southern Baltic zoobenthos, the blue mussel Mytilus trossulus.
Proteins were isolated by precipitation from homogenised mussel
hepatopancreases. The protein samples were heated
(70 oC)
and acidified (pH 4.5). Then the proteins with a molecular weight
close to that of plant ferritin
were separated by ultracentrifugation. These preparations were compared using
capillary electrophoresis with plant ferritins isolated from lupin
(Lupinus luteus) and amaranth (Amaranthus hybridus). The
electrophoregrams obtained revealed that the hepatopancreas of
the Baltic blue mussel (Mytilus trossulus) contains a
protein displaying the properties of plant ferritin.
Sergey I. Pogosyan
Department of Biophysics, Faculty of Biology, Moscow State University,
Moscow
Marina A. Sivchenko, Viktor N. Maximov
Department of Ecology and Invertebrate Zoology, Faculty of Biology,
Moscow State University, Moscow
Mirosława Ostrowska
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences,
Sopot
Physiological heterogeneity of an algal population: classification of
Scenedesmus quadricauda cenobia by the features of their
photosynthetic apparatus
Oceanologia
1997, no. 39 (2), pp. 163-175
Keywords: Chlorophyll; Fluorescence; Induction curves cluster analysis
Manuscript received April 25, 1997, in final form June 12, 1997.
Abstract
An analysis of the typological composition of individual
cenobia of the microalga Scenedescemus quadricauda using
typification of chlorophyll fluorescence induction curves is
presented. Cluster analysis was applied to separate various
types of induction curves. The 12 representative types of
fluorescence induction curves of S. quadricauda are given.
The possibility of division into separate clusters
confirms the assumption of the
discrete states of the photosynthetic apparatus. The connection
between the functional structure of the population and its
growth stage can be established.
Justyna Miac, Małgorzata Groth, Maciej Wołowicz
Institute of Oceanography, Gdańsk University, Gdynia
Seasonal changes in the Mya arenaria (L.) population from
Inner Puck Bay
Oceanologia
1997, no. 39 (2), pp. 177-195
Keywords: Mya arenaria; Population dynamics; Biochemical composition;
Inner Puck Bay
Manuscript received April 4, 1997, in final form May 20, 1997.
Abstract
Morphometric relationships, the growth rate, sex distribution and annual fluctuation in dry flesh weight, biochemical composition and energy value of the sublittoral bivalve Mya arenaria (L.) from
Inner Puck Bay were studied from May 1994 to April 1995.
M. arenaria grows rapidly during the first year of its life, after which the growth rate decreases. The oldest individual was 5 years old and 53 mm long. Judging from the sex distribution and analysis of biochemical
composition, the soft-shell clam breeds in June-July. Analysis of the growth rate and the age distribution confirms the theories that specimens of M. arenaria found in low latitudes reach a smaller maximum size
and grow more slowly than those living in higher latitudes.
The biochemical composition was determined in the 20-30 mm length class.
The mean percentages of the main components of dry flesh were: proteins
47.54  6.0 (male),
51.28
6.0 (male),
51.28  7.7 (female); carbohydrates
9.28
7.7 (female); carbohydrates
9.28  3.7 (male),
10.40
3.7 (male),
10.40  4.0 (female); glycogen
5.74
4.0 (female); glycogen
5.74  2.8 (male), 6.72
2.8 (male), 6.72  3.5 (female); lipids
8.67
3.5 (female); lipids
8.67  1.8 (male), 8.79
1.8 (male), 8.79  1.3 (female).
Analysis of lipid and carbohydrate (glycogen) content in tissues of the
soft-shell clam yielded the highest values in the residue
(gonads and hepatopancreas). The lipid level is much higher in early spring,
before spawning, than in autumn, when gonad development begins.
The highest energy values are reported for August
(20.82 J mg-1 in both
sexes), the lowest for October
(14.38 J mg-1 in males and 14.98 J mg-1 in
females). Seasonal changes in energy values are mainly connected with the
availability of food and reproduction cycle.
1.3 (female).
Analysis of lipid and carbohydrate (glycogen) content in tissues of the
soft-shell clam yielded the highest values in the residue
(gonads and hepatopancreas). The lipid level is much higher in early spring,
before spawning, than in autumn, when gonad development begins.
The highest energy values are reported for August
(20.82 J mg-1 in both
sexes), the lowest for October
(14.38 J mg-1 in males and 14.98 J mg-1 in
females). Seasonal changes in energy values are mainly connected with the
availability of food and reproduction cycle.
Chronicle
Henryk Gurgul
Marine Physics Department, University of Szczecin, Szczecin
Henryk Arctowski and Antoni Dobrowolski in the hundreth
anniversary of 'Belgica' expedition to Antarctica
Oceanologia
1997, no. 39 (2), pp. 197-199
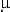 g Cd dm-3)
or radiocadmium (9 kBq 115mCd dm-3) and humic substances (0.0-7.2 mg HS dm-3).
Experiments were carried out in seawater at two different constant
temperatures (6oC
g Cd dm-3)
or radiocadmium (9 kBq 115mCd dm-3) and humic substances (0.0-7.2 mg HS dm-3).
Experiments were carried out in seawater at two different constant
temperatures (6oC  1oC or 15oC
1oC or 15oC  1oC).
The exposure time ranged from 8 to 21 days.
It was found that marine humic substances stimulate cadmium accumulation
by the mussels; however, the effect was strongly modified
by temperature. At 6oC
cadmium was preferably accumulated in the gills while at 15oC
the metal was stored mainly in the hepatopancreas. Two pools
of cadmium accumulated by Mytilus trossulus were detected.
Cadmium adsorbed to the shell was desorbed quickly and efficiently after the
mussels, previously grown in seawater containing an elevated metal concentration
(8 days, 50
1oC).
The exposure time ranged from 8 to 21 days.
It was found that marine humic substances stimulate cadmium accumulation
by the mussels; however, the effect was strongly modified
by temperature. At 6oC
cadmium was preferably accumulated in the gills while at 15oC
the metal was stored mainly in the hepatopancreas. Two pools
of cadmium accumulated by Mytilus trossulus were detected.
Cadmium adsorbed to the shell was desorbed quickly and efficiently after the
mussels, previously grown in seawater containing an elevated metal concentration
(8 days, 50 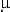 g Cd dm-3 or 9 kBq 115m Cd dm-3),
had been transferred to natural seawater (60 days, 0.03
g Cd dm-3 or 9 kBq 115m Cd dm-3),
had been transferred to natural seawater (60 days, 0.03 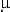 g Cd dm-3, 0 kBq 115m Cd dm-3).
The other pool of cadmium, accumulated in
the soft tissue of the mussels, remained intact after depuration
experiments lasting several weeks. Humic substances had no
effect on the depuration of cadmium from either pool.
g Cd dm-3, 0 kBq 115m Cd dm-3).
The other pool of cadmium, accumulated in
the soft tissue of the mussels, remained intact after depuration
experiments lasting several weeks. Humic substances had no
effect on the depuration of cadmium from either pool.
 6.0 (male),
51.28
6.0 (male),
51.28  7.7 (female); carbohydrates
9.28
7.7 (female); carbohydrates
9.28  3.7 (male),
10.40
3.7 (male),
10.40  4.0 (female); glycogen
5.74
4.0 (female); glycogen
5.74  2.8 (male), 6.72
2.8 (male), 6.72  3.5 (female); lipids
8.67
3.5 (female); lipids
8.67  1.8 (male), 8.79
1.8 (male), 8.79  1.3 (female).
Analysis of lipid and carbohydrate (glycogen) content in tissues of the
soft-shell clam yielded the highest values in the residue
(gonads and hepatopancreas). The lipid level is much higher in early spring,
before spawning, than in autumn, when gonad development begins.
The highest energy values are reported for August
(20.82 J mg-1 in both
sexes), the lowest for October
(14.38 J mg-1 in males and 14.98 J mg-1 in
females). Seasonal changes in energy values are mainly connected with the
availability of food and reproduction cycle.
1.3 (female).
Analysis of lipid and carbohydrate (glycogen) content in tissues of the
soft-shell clam yielded the highest values in the residue
(gonads and hepatopancreas). The lipid level is much higher in early spring,
before spawning, than in autumn, when gonad development begins.
The highest energy values are reported for August
(20.82 J mg-1 in both
sexes), the lowest for October
(14.38 J mg-1 in males and 14.98 J mg-1 in
females). Seasonal changes in energy values are mainly connected with the
availability of food and reproduction cycle.