Oceanologia No. 38 (4) / 96
Contents
Papers
Dissertations
Chronicle
Papers
Jolanta Kuśmierczyk-Michulec, Miroslaw Darecki
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
The aerosol optical thickness over the Baltic Sea
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (4), pp. 423-435
Keywords: Baltic Sea; Aerosol optical thickness; Empirical orthogonal
functions; Air temperature; Visible spectrum
Manuscript received June 6, 1996, in final form September 7, 1996.
Abstract
The results of applying empirical orthogonal functions (EOF)
to the decomposition and approximation of spectra of the aerosol
optical thickness are presented. The aerosol optical thickness
is calculated on the basis of the experimental data of
the direct and diffuse irradiances collected on cloudless
days in 1993 and 1994 over the southern Baltic Sea.
The main finding is that the amplitude of aerosol
optical thickness in the visible spectrum is dependent on air
temperature.
Jolanta Kuśmierczyk-Michulec
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
The standard CZCS algorithm: found to be inappropriate for the atmosphere
over the Baltic Sea
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (4), pp. 437-445
Keywords: Baltic Sea; Aerosol radiance; Water-leaving radiance;
Case 1 Waters; Case 2 Waters
Manuscript received August 28, 1996, in final form November 28, 1996.
Abstract
In the standard CZCS atmospheric correction method the aerosol radiance
is derived on the assumption that the water-leaving radiance at 670 nm
is zero. This assumption, justified for water whose reflectance is
determined solely by absorption (Case 1 Waters), gives rise to errors
where the reflectance of the water is significantly influenced by
scattering (Case 2 Waters), e.g. the Baltic Sea.
The values of the aerosol radiance are too high and those of
water-leaving radiance too low in comparison with the experimental
ones. The relative error for the aerosol radiances (normalised to
their values at 670 nm) decreases with wavelength from 60% at
443 nm to 13% at 550 nm.
Sławomir B. Woźniak
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Mathematical spectral model of solar irradiance reflectance and transmittance
by a wind-ruffled sea surface. Part 1. The physical problem and mathematical
apparatus
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (4), pp. 447-467
Keywords: Sea surface reflectance; Sea surface transmittance
Manuscript received September 10, 1996, in final form October 28, 1996.
Abstract
A spectral model of solar irradiance reflectance from
and transmittance through
a wind-ruffled sea surface is developed in two papers. This, the first paper,
discusses the mathematical apparatus of the model. Dependences for sea surface
slope distribution (based on Cox and Munk, 1954) and the foam coverage of the
sea surface (based on Gordon and Jacobs, 1977), both these distributions
having been modified by the author, were used in the modelling.
Being direct functions of a dynamic factor,
i.e. the mean height of the waves 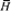 , they take the
influence of environmental
(hydrometeorological and geometrical) factors into account.
The Snell and Fresnel
laws were applied to the light transmission through the surface. Polarisation
effects were neglected.
, they take the
influence of environmental
(hydrometeorological and geometrical) factors into account.
The Snell and Fresnel
laws were applied to the light transmission through the surface. Polarisation
effects were neglected.
Tomasz Petelski, Maria Chomka
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Marine aerosol fluxes in the coastal zone - BAEX experimental data
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (4), pp. 469-484
Keywords: Aerosol; Flux; Breaker zone
Manuscript received June 26, 1996, in final form September 6, 1996.
Abstract
This paper presents the results of investigations
designed to determine the exchange processes between the sea
and the air above the coastal zone.
The calculations were carried out using experimental data collected
by impactor measurements of the marine aerosol above the
coastal zone during the Baltic Aerosol Experiment - I and II (BAEX-I, II).
Andrzej Jankowski
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Vertical water circulation in the southern Baltic
and its environmental implications
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (4), pp. 485-503
Keywords: Southern Baltic; Gdańsk and Bornholm Deeps;
Vertical water circulation; Environmental consequences
Manuscript received June 21, 1996, in final form August 6, 1996.
Abstract
A simple method of estimating the vertical current vector velocity
component w
based on the water shear stress vorticity equation is presented and briefly
discussed. Spatial distributions of the mean climatic values of w
for selected months calculated from the averaged multi-year
observations of atmospheric pressure and water density (diagnostic approach)
in the southern Baltic Sea are investigated.
The results show the existence of `permanent' (during the year)
zones of upwelling and downwelling in the region of the Baltic Deeps
related to the clockwise and anticlockwise gyres observed on the charts
of calculated horizontal currents. These characteristic features of the
horizontal and vertical water movements in the region of the Gdańsk and
Bornholm Deeps may be important for the ecological, biological and geological
understanding of the region as well as in the context of the pollution problem,
especially during stagnation periods.
Kurt Frischmuth
Department of Mathematics, Rostock University, Rostock
Andrzej Jankowski
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Estimation of the period of free oscillations
(seiches) in the Kirrbucht
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (4), pp. 505-528
Keywords: Kirrbucht; Seiches; Numerical modelling
Manuscript received July 15, 1996, in final form September 18, 1996.
Abstract
An attempt was made to estimate the periods of the main seiches
in the Kirrbucht, a shallow water basin with an irregular coastline.
A quasi-linear hydrodynamic-numerical model of the storm surges
(wind-driven circulation) in a shallow density-homogeneous basin was used.
The results of calculations of sea level oscillations generated in the basin
in response to a temporally and spatially constant wind field (stress)
were treated as a time series in order that the seiche periods
could be calculated.
The standard discrete Fourier transformation was applied to estimate amplitude
spectra. The periods of the three significant modes were found to be equal
to 3.21 min, 4.94 min and 6.59 min. The latter two are probably fundamental
ones: they are the transverse and longitudinal modes respectively.
The influence of non-linear terms and lateral fricton on
the seiche periods is also discussed.
Andrzej Wroblewski
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Seasonal forcing of Baltic water volumes by the meteorological fields over
the basin from 1896 to 1970
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (4), pp. 529-541
Keywords: Baltic Sea level; Atmospheric pressure; Seasonal oscillations
Manuscript received June 28, 1996, in final form September 6, 1996.
Abstract
This paper discusses the seasonal oscillations of the meteorological fields
influencing the seasonal changes in the Baltic water balance. Mean monthly
atmospheric pressure data (1896-1970) from eight stations located around
the Baltic were taken to be the basis for the computations. Six horizontal
components of the atmospheric pressure gradients were selected for use in the
subsequent computations. The mean monthly water volumes in the Baltic were
computed by the method presented by the author in an earlier publication
(Wroblewski, 1992a). In the next step, the selected horizontal components
of atmospheric pressure gradients were expanded into EOFs. The first three
amplitude expansion functions of the wind field had more significant coherences
with changes in the Baltic water volumes than the corresponding
EOF functions of
the atmospheric pressure field. The spectral and statistical analysis of these
functions and gradients was computed in order to detect their periodic
structure and statistical characteristics. The multiple input stochastic
dynamic system was used in the analysis. The most important result is the
demonstration that the solar annual period is distinct in the wind-field
components
influencing the sea's seasonal dynamics. The solar semi-annual period is not well
marked. The mean atmospheric pressure over the Baltic has a weak seasonal
structure and practically does not force the water volume changes.
Waldemar Surosz
Institute of Oceanography, Gdańsk University, Gdynia
Alicja Kosakowska
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Effects of siderophores and amino acids on the growth and photosynthesis
of populations of Chlorella vulgaris Beijerinck and
Anabaena variabilis Kutzing
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (4), pp. 543-552
Keywords: Chlorella vulgaris; Anabaena variabilis ; Siderophores;
Amino acids; Chlorophyll a; Photosynthesis
Manuscript received June 28, 1996, in final form September 16, 1996.
Abstract
The object of this paper was to determine whether the presence of the amino
acids and siderophores tested is important to the growth and photosynthesis
of phytoplanktonic cells cultivated under iron deficiency conditions, and can
thus shed light on the function of two groups of natural
chelating agents
in the aquatic environment. The results obtained indicate that the siderophoric
substances and amino acids can modify physiological processes in populations
of cells of cyanobacteria and green algae.
Dissertations
Joanna Kozuch
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
The effect of selected properties of humic acids on cadmium uptake
in the mollusc Mytilus trossulus
(review by A. Szaniawska)
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (4), pp. 553-554
Ph. D. thesis in biological oceanography
supervised by Associate Professor Janusz Pempkowiak.
Chronicle
Jerzy Dera
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Professor Czesław Druet - on the occasion of his 70th birthday
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (4), pp. 555-558
 Back to IO PAS Home Page
Back to IO PAS Home Page
 Sabina Szczykowska <sabina@iopan.gda.pl>
Sabina Szczykowska <sabina@iopan.gda.pl>
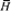 , they take the
influence of environmental
(hydrometeorological and geometrical) factors into account.
The Snell and Fresnel
laws were applied to the light transmission through the surface. Polarisation
effects were neglected.
, they take the
influence of environmental
(hydrometeorological and geometrical) factors into account.
The Snell and Fresnel
laws were applied to the light transmission through the surface. Polarisation
effects were neglected.
 Back to IO PAS Home Page
Back to IO PAS Home Page