Oceanologia No. 38 (3) / 96
Contents
Papers
Communications
Reviews
Papers
Anna Rozwadowska
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Influence of clouds on the broadband spectral
irradiance at the Baltic surface
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (3), pp. 297-315
Keywords: Baltic atmosphere; Broadband spectral irradiance; Clouds
Manuscript received May 14, 1996, in final form June 21, 1996.
Abstract
On the basis of downward irradiance data in the ultraviolet,
visible and infrared spectral intervals as well as of meteorological
observations collected during several cruises to the Baltic,
the influence of clouds and solar zenith angle
on the broadband spectral composition of solar radiation
reaching the Baltic surface is analysed. The relation
between the atmospheric transmittance of total irradiance
and solar zenith angle, and the ratios of broadband spectral
irradiance to the total for both visible
and infrared radiation have been estimated by polynomials.
Sławomir B. Woźniak
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Sea surface slope distribution and foam coverage
as functions of the mean height of wind waves
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (3), pp. 317-332
Keywords: Wind waves; Slope distribution; Foam coverage;
Mean wave height; Modified Cox-Munk expression;
Modified Gordon-Jacobs expression
Manuscript received April 9, 1996, in final form May 29, 1996.
Abstract
The article discusses problems of the statistical description
of a wind-ruffled sea surface for optical modelling purposes.
A new parameter, namely the mean height of the waves 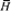 ,
is used in both the slope distribution of the ruffled sea surface and the
foam coverage of the surface. Unlike the parameter used up to
the present, i.e. the wind speed over the sea surface v, the mean
height of the waves
,
is used in both the slope distribution of the ruffled sea surface and the
foam coverage of the surface. Unlike the parameter used up to
the present, i.e. the wind speed over the sea surface v, the mean
height of the waves 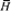 is connected with a large
number of hydrometeorological and
geometrical factors modifying the state of wave motion of the sea
(e.g. the wind fetch D, the sea depth h, the shape of the coastal
region etc.). A theoretical basis for applying this new parameter
and modifying dependences for the slope distribution and the foam coverage
of the ruffled sea surface is given. In addition this paper contains
an initial verification of the ideas presented with the small number
of data available in the literature.
is connected with a large
number of hydrometeorological and
geometrical factors modifying the state of wave motion of the sea
(e.g. the wind fetch D, the sea depth h, the shape of the coastal
region etc.). A theoretical basis for applying this new parameter
and modifying dependences for the slope distribution and the foam coverage
of the ruffled sea surface is given. In addition this paper contains
an initial verification of the ideas presented with the small number
of data available in the literature.
Jadwiga Mrozek-Lejman, Grażyna Karbowniczek-Gratkowska
Marine Physics Department, University of Szczecin,
Szczecin
The position of the seasonal thermocline in southern Baltic
waters polluted with crude oil
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (3), pp. 333-349
Keywords: Seasonal thermocline; Eutrophic seawater; Crude oil pollution
Manuscript received March 5, 1996, in final form June 7, 1996.
Abstract
The paper deals with the formation of the thermocline and the mixed layer
in a sea polluted with crude oil when the natural optical parameters of
eutrophic seawater are seasonally variable. Differentiation of the degree
of eutrophication of the seawater is expressed in terms of the concentrations
of chlorophyll and yellow substances. The occurrence of crude oil pollution
is taken into account by modifying the time-variable absorption coefficient
of the seawater - crude oil system. The variability in the absorption spectra
of natural seawater in the spring - summer season is estimated on the basis of
investigations of seasonal changes in the chlorophyll concentration in the
southern Baltic.
Numerical simulations were carried out for Baltic and Gulffax crude oil
using the one-dimensional integral DKTz-2 model. The computations were
performed for monthly average values of parameters determining the state of
the southern Baltic environment collected over several years. Experimentally
found crude-oil optical parameters (light refraction and absorption coefficients)
were applied, as were the variability with time of these parameters and that
of the crude oil layer thickness.
The results of the numerical simulations show that the increase in the
volumetric concentration of crude oil in the upper sea layer causes
the thermocline
to be formed closer to the water surface. Simultaneously, the thickness of the
mixed layer decreases but its temperature rises. If a crude oil layer appears
on the water surface, the trend of the changes is the same.
Amany Mohamed Haroon
Academy of Scientific Research and Technology,
National Institute of Oceanography and Fisheries, Cairo
Anna Szaniawska
Institute of Oceanography, Gdańsk University, Gdynia
Comparative estimations of the energy content of Enteromorpha spp.
using different methods
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (3), pp. 351-360
Keywords: Enteromorpha spp.; Comparative determination; Energy content;
Jurata
Manuscript received March 4, 1996, in final form May 28, 1996.
Abstract
The energy content of Enteromorpha spp. from Jurata (situated in
the western part of the Gulf of Gdańsk) was determined. The values
were measured directly by combustion in a microbomb calorimeter and indirectly
by calculation based on the biochemical composition, and on carbon and nitrogen
contents.
On the basis of the results obtained, very little difference - on average
2.98  5.69% (0.54
5.69% (0.54  0.67 J mg-1 of DW) - was found between the
energy values calculated from the carbon content and those calculated from
carbon and nitrogen contents. Moreover, the values calculated from both these
sources were higher those that calculated from the biochemical composition
by about 14.95
0.67 J mg-1 of DW) - was found between the
energy values calculated from the carbon content and those calculated from
carbon and nitrogen contents. Moreover, the values calculated from both these
sources were higher those that calculated from the biochemical composition
by about 14.95  12.24% (2.09
12.24% (2.09  1.72 J mg-1 of DW) and
17.28
1.72 J mg-1 of DW) and
17.28  14.41% (2.63
14.41% (2.63  2.07 J mg-1 of DW) for the two methods
respectively. At the same time, large differences were found between the
values calculated using microbomb calorimetry and other methods (biochemical
composition, carbon content, and carbon and nitrogen contents): they were
20.40
2.07 J mg-1 of DW) for the two methods
respectively. At the same time, large differences were found between the
values calculated using microbomb calorimetry and other methods (biochemical
composition, carbon content, and carbon and nitrogen contents): they were
20.40  15.09%, 33.76
15.09%, 33.76  5.86% and 35.74
5.86% and 35.74  6.71% for the three
methods respectively.
6.71% for the three
methods respectively.
Ashraful Mohammed Haque
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Maria Szymelfenig
Institute of Oceanography, Gdańsk University, Gdynia
Jan Marcin Węsławski
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
The sandy littoral zoobenthos of the Polish Baltic coast
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (3), pp. 361-378
Keywords: Baltic littoral; Benthos
Manuscript received January 26, 1996, in final form May 20, 1996.
Abstract
Macrobenthos and meiobenthos were quantitatively sampled in the
sandy littoral along the Polish Baltic Sea coast in August 1994.
Macrofaunal abundance (0-987 indiv. m-2), biomass (0-3.19 g m-2
wet wt.) and the number of species (3) were very low.
Eight meiofaunal animal groups were found.
Meiofaunal abundance (38-760 indiv. 10-1 cm-2) was dominated by
Nematoda and Turbellaria, the biomass (0.86-34.9 mg 10-1 cm-2
wet wt.) by Oligochaeta. In terms of biomass, the macrobenthos:meiobenthos
ratio ranged from 0.02 to 5.17. Macrofaunal abundance and biomass
were more variable than those of the meiofauna.
Maria Włodarska-Kowalczuk
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Urszula Janas, Anna Szaniawska
Institute of Oceanography, Gdańsk University, Gdynia
Hydrogen sulphide and other factors influencing the macrobenthic community
structure in the Gulf of Gdańsk
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (3), pp. 379-394
Keywords: Gulf of Gdańsk; Macrofaunal communities; Hydrogen sulphide; Biodiversity
Manuscript received May 8, 1996, in final form July 24, 1996.
Abstract
Three stations in the Gulf of Gdańsk were sampled monthly for one year
with regard to macrozoobenthos composition, oxygen content and temperature
of near-bottom waters, granulometry, organic matter content and
H2S concentration in sediments. The differences in
H2S concentrations at the stations were most
conspicious. The presence and concentrations of H2S appeared to be the
decisive factor for the grouping of samples in the Bray-Curtis Similarity
Index-based ordination. Even seasonality was of secondary importance.
The number of species and the Shannon Indices decreased, and the dominance of the
predominant species - Macoma balthica - increased in accordance with
the H2S gradient between the stations. The community was dominated by
detritus-feeders.
Communications
Waldemar Grzybowski
Institute of Oceanography, Gdańsk University, Gdynia
Preliminary results of dissolved organic carbon concentration
measurements in the
Vistula river mouth using high-temperature catalytic oxidation
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (3), pp. 395-403
Keywords: Salinity; Dissolved organic carbon; High-temperature catalytic oxidation;
Gulf of Gdańsk
Abstract
Some 100 measurements of dissolved organic carbon (DOC)
concentrations were made in the water in the Vistula river
mouth area using high-temperature catalytic oxidation. The results
ranged from 4.8 to 22.4 mg dm-3. No relationship was detected
between DOC and salinity within the 0.9-7.6 PSU salinity range.
Anna Wasik, Ewa Mikołajczyk
Department of Cell Biology, Nencki Institute of Experimental Biology,
Polish Academy of Sciences, Warsaw
The seasonal succession of hyaline Helicostomella subulata and agglutinated Tintinnopsis lobiancoi - dominants of the Baltic
Tintinnina (Ciliophora)
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (3), pp. 405-418
Keywords: Baltic Sea; Helicostomella subulata; Tintinnids; Tintinnopsis lobiancoi
Abstract
Tintinnid species composition and abundance were
determined in surface water samples taken from four sites in the
Gulf of Gdańsk,
and along four cruise tracks from the Gulf of Gdańsk to Helsinki.
The seasonal succession of two dominants - the hyaline Helicostomella
subulata
and the agglutinated Tintinnopsis lobiancoi - was evident.
The former coincided with the beginning of summer and was replaced
early in the season by the latter. Other Tintinnina species were found
only occasionally and did not significantly affect the total
tintinnid abundance.
Reviews
Jerzy Dera
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Underwater irradiance as a factor affecting primary production
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (3), pp. 419-422
by Jerzy Dera, Dissertations and monographs IO PAS, 7, 1995;
110 pp. (68 + 42 in Appendix), 14 figures (13 + 1), 44 tables (4 + 36).
 Back to IO PAS Home Page
Back to IO PAS Home Page
 Sabina Szczykowska <sabina@iopan.gda.pl>
Sabina Szczykowska <sabina@iopan.gda.pl>
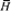 ,
is used in both the slope distribution of the ruffled sea surface and the
foam coverage of the surface. Unlike the parameter used up to
the present, i.e. the wind speed over the sea surface v, the mean
height of the waves
,
is used in both the slope distribution of the ruffled sea surface and the
foam coverage of the surface. Unlike the parameter used up to
the present, i.e. the wind speed over the sea surface v, the mean
height of the waves 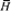 is connected with a large
number of hydrometeorological and
geometrical factors modifying the state of wave motion of the sea
(e.g. the wind fetch D, the sea depth h, the shape of the coastal
region etc.). A theoretical basis for applying this new parameter
and modifying dependences for the slope distribution and the foam coverage
of the ruffled sea surface is given. In addition this paper contains
an initial verification of the ideas presented with the small number
of data available in the literature.
is connected with a large
number of hydrometeorological and
geometrical factors modifying the state of wave motion of the sea
(e.g. the wind fetch D, the sea depth h, the shape of the coastal
region etc.). A theoretical basis for applying this new parameter
and modifying dependences for the slope distribution and the foam coverage
of the ruffled sea surface is given. In addition this paper contains
an initial verification of the ideas presented with the small number
of data available in the literature.
 5.69% (0.54
5.69% (0.54  0.67 J mg-1 of DW) - was found between the
energy values calculated from the carbon content and those calculated from
carbon and nitrogen contents. Moreover, the values calculated from both these
sources were higher those that calculated from the biochemical composition
by about 14.95
0.67 J mg-1 of DW) - was found between the
energy values calculated from the carbon content and those calculated from
carbon and nitrogen contents. Moreover, the values calculated from both these
sources were higher those that calculated from the biochemical composition
by about 14.95  12.24% (2.09
12.24% (2.09  1.72 J mg-1 of DW) and
17.28
1.72 J mg-1 of DW) and
17.28  14.41% (2.63
14.41% (2.63  2.07 J mg-1 of DW) for the two methods
respectively. At the same time, large differences were found between the
values calculated using microbomb calorimetry and other methods (biochemical
composition, carbon content, and carbon and nitrogen contents): they were
20.40
2.07 J mg-1 of DW) for the two methods
respectively. At the same time, large differences were found between the
values calculated using microbomb calorimetry and other methods (biochemical
composition, carbon content, and carbon and nitrogen contents): they were
20.40  15.09%, 33.76
15.09%, 33.76  5.86% and 35.74
5.86% and 35.74  6.71% for the three
methods respectively.
6.71% for the three
methods respectively.
 Back to IO PAS Home Page
Back to IO PAS Home Page