Oceanologia No. 37 (1) / 95
Contents
Papers
Reviews
Dissertations
Papers
Sergey V. Semowski, Bogdan Woźniak
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Model of the annual phytoplankton cycle in the marine ecosystem-assimilation of monthly satellite chlorophyll data for the North Atlantic and Baltic
Oceanologia 1995, no. 37 (1), pp. 3-31
Keywords: Marine ecosystem; Phytoplankton; Dynamics modelling; Primary
production; Remote sensing
Manuscript received November 23, 1994, in final form January 25, 1995.
Abstract
An annual-cycle model for the phytoplankton-zooplankton-nutrients ecosystem is
presented for the North Atlantic and Baltic Sea. Satellite-derived surface
chlorophyll data assimilation in the ecosystem model are discussed, and a number
of methods of fitting model dynamics to the data are proposed. Statistical
analysis of simulation results yields the main types of annual chlorophyll and
primary production variability.
Jolanta Kuśmierczyk-Michulec
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
A semi-empirical expression for the solar spectral diffuse irradiance
at the sea surface
Oceanologia 1995, no. 37 (1), pp. 33-45
Keywords: Diffuse irradiance; Southern Baltic Sea; Aerosol optical thickness
Manuscript received November 7, 1994, in final form January 12, 1995.
Abstract
A simple, semi-empirical expression, valid in the visible spectrum for
calculations of the solar diffuse irradiance, is presented. This relation
is based on experimental data collected on cloudless days in 1993 and 1994
over the southern Baltic Sea. In order to illustrate the accuracy of the
proposed formula, the aerosol optical thickness is calculated. The
semi-empirical diffuse irradiance model can be used to make accurate calculations of the solar spectral diffuse irradiance and the aerosol optical thickness.
Jan Piechura, Waldemar Walczowski
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
The Arctic Front: structure and dynamics
Oceanologia 1995, no. 37 (1), pp. 47-73
Keywords: Water masses; Front; Dynamics
Manuscript received January 4, 1995, in final form February 2, 1995.
Abstract
During summer expeditions of r/v "Oceania" to the Arctic Seas, the Arctic
Front has been crossed and investigated each time since 1987. The 1993 cruise
initiated more detailed investigations of this phenomenon. In the area
delimited by longitudes 2o41'W and 3o05'E and
latitudes 70o54'N and 72o32'N, five CTD transects were
done with the CTD cast every 5 or 2 nm on each transect.
The location and direction of the front have been defined. The geostrophic component of the general circulation shows good agreement with the earlier
data: a strong current (up to 40 cm s-1) on the Atlantic side of
the front, about zero velocity in the middle and a weak current (5-10 cm
s-1) on the Arctic side of the front. The steepest horizontal
gradients were ca 0.5oC km-1 (temperature) and
ca 0.04 psu km-1 (salinity). The data reveal the complicated
structure of the front with its intrusions, meanders and gyres.
Maciej Matciak, Jacek Nowacki
Institute of Oceanography, Gdańsk University, Gdynia
The Vistula river discharge front - surface observations
Oceanologia 1995, no. 37 (1), pp. 75-88
Keywords: Plume front; Surface water properties; River Vistula
Manuscript received December 8, 1994, in final form February 27, 1995.
Abstract
The spreading of Vistula river
water has been studied
on the basis of surface spatial distributions of
water properties.
The horizontal divergence field of the gradient of a given property is
analysed to find the main directions of surface water transport.
This shows that advection in the direction
perpendicular to the frontal line is weak. Examples of
salinity, temperature (AVHRR/SST), density and nutrient
concentration fields
in the area adjacent to the river mouth are discussed.
Grażyna Kowalewska
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Metalloporphyrins in recent sediments of the Baltic Sea
Oceanologia 1995, no. 37 (1), pp. 89-98
Keywords: Metalloporphyrins; Nickel(II); Vanadyl(II); Sediments;
Sea; Baltic
Manuscript received February 3, 1995, in final form March 21, 1995.
Abstract
Recent sediments of the southern Baltic Sea were investigated for the
possible occurrence of metalloporphyrins. The content of both
vanadyl(II) and nickel(II) metalloporphyrins estimated in the
sediment samples studied is of the order of magnitude (1-6)
x 10-2 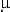 g g-1 (d. w.). The results also suggest that the porphyrins
in recent Baltic sediments are of anthropogenic origin.
The highly significant correlation of the metalloporphyrin content
with chlorophyll a indicates either that these
metalloporphyrins are formed in the water column or
that phytoplankton contribute to metalloporphyrin transfer from
water to sediments.
g g-1 (d. w.). The results also suggest that the porphyrins
in recent Baltic sediments are of anthropogenic origin.
The highly significant correlation of the metalloporphyrin content
with chlorophyll a indicates either that these
metalloporphyrins are formed in the water column or
that phytoplankton contribute to metalloporphyrin transfer from
water to sediments.
Amany Mohamed Haroon
Academy of Scientific Research and Technology, National Institute of
Oceanography and Fisheries, 101 Kaser El-eni St., Cairo, Egypt
Anna Szaniawska, Waldemar Surosz
Institute of Oceanography, Gdańsk University, Gdynia
Changes in heavy metal accumulation in Enteromorpha spp. from the Gulf of Gdańsk
Oceanologia 1995, no. 37 (1), pp. 99-110
Keywords: Enteromorpha spp.; Heavy metals; Gulf of Gdańsk
Manuscript received December 20, 1994, in final form March 9, 1995.
Abstract
The contents of Cu, Zn, Cd,
and Pb were determined in samples of Enteromorpha spp. collected at Jurata at monthly intervals from November 1992 to October 1993, and at different
stations on the coast of the Gulf of Gdańsk during one month.
Of all the metals analysed, Zn occurs in the highest concentrations,
followed by Cu, Pb and Cd. In the samples from Jurata all the four
metals displayed considerable seasonal variations in their concentrations,
the ranges for each element being Zn - 29.80-90.05 µg-1 dry wt.,
Cu - 12.82-28.41 µg-1 dry wt., Pb - 1.81-7.08
µg-1 dry wt. and Cd - 0.08-0.51 µg-1 dry wt. The
highest concentrations of all elements except Pb were recorded in
November 1992.
Different concentrations of these metals were recorded
in Enteromorpha spp. collected at different stations
on the same day; the highest concentrations of Zn,
Cu, and Pb were found in samples from Jastarnia (Zn - 72.11
µg-1 dry wt., Cu - 48.19 µg-1 dry wt. and Pb - 9.41
µg-1 dry wt.), and from Gdynia (Zn - 65.29 µg-1 dry
wt., Cu - 29.13 µg-1 dry wt. and Pb - 5.72 µg-1 dry
wt.). This implies a high level of pollution
at these stations in comparison with the others. The highest
concentration of Cd was recorded in samples from Puck (0.43
µg-1 dry wt.).
Aldona Dobrzycka, Anna Szaniawska
Institute of Oceanography, Gdańsk University, Gdynia
The effect of salinity on osmoregulation in Corophium volutator (Pallas)
and Saduria entomon (Linnaeus) from the Gulf of Gdańsk
Oceanologia 1995, no. 37 (1), pp. 111-122
Keywords: Osmoregulation; Salinity; Corophium volutator; Saduria entomon; Gulf of Gdańsk
Manuscript received January 30, 1995, in final form March 24, 1995.
Abstract
Material for the study was collected in the summer of
1994 in the Gulf of Gdańsk where specimens of Corophium
volutator and Saduria entomon - organisms living in a zone of critical
salinity (5-8 psu) - commonly occur.
The high osmolarity of their body fluids
is indicative of their adaptation effort to the salinity in their habitat.
A species of marine origin, Corophium volutator maintains its osmotic concentration of haemolymph at a high level, as
other species in brackish waters do; however, this is not the
case with Corophium volutator specimens living in saline seas. Saduria entomon - a relict
of glacial origin, originally from the Arctic Sea - also maintains a
high osmotic concentration of haemolymph in comparison with
specimens of this species living in the Beaufort Sea.
Marcin Pliński
Institute of Oceanography, Gdańsk University, Gdynia
Phytoplankton of the Gulf of Gdańsk in 1992 and 1993
Oceanologia 1995, no. 37 (1), pp. 123-135
Keywords: Phytoplankton; Seasonal changes; Distribution; Gulf of Gdańsk
Manuscript received December 13, 1994, in final form May 31, 1995.
Abstract
The article presents the results of a quantitative analysis
of phytoplankton in the
Gulf of Gdańsk from samples taken in 1992 and 1993. The quantity
of phytoplankton
was higher in 1993 than in 1992. The greatest difference in cell numbers
between the two years was
found among the diatoms. A high number of dinoflagellates was observed
during spring in both years.
Reviews
Andrzej Icha
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
The theory of turbulence in stratified media
Oceanologia 1995, no. 37 (1), pp. 137-139
by Andrzej Icha (ed.),
Institute of Oceanology PAS,
1994, 227 pp., 2 figures, (in Polish).
Dissertations
Sławomir Kwaśniewski
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Mesozooplankton distribution in the epipelagial of the Norwegian-Barents
Seas boundary in summer
Oceanologia 1995, no. 37 (1), pp. 141-141
Ph. D. thesis in biological oceanography supervised by Professor Krystyna Wiktor.
 Back to IO PAS Home Page
Back to IO PAS Home Page
 Sabina Szczykowska <sabina@iopan.gda.pl>
Sabina Szczykowska <sabina@iopan.gda.pl>
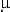 g g-1 (d. w.). The results also suggest that the porphyrins
in recent Baltic sediments are of anthropogenic origin.
The highly significant correlation of the metalloporphyrin content
with chlorophyll a indicates either that these
metalloporphyrins are formed in the water column or
that phytoplankton contribute to metalloporphyrin transfer from
water to sediments.
g g-1 (d. w.). The results also suggest that the porphyrins
in recent Baltic sediments are of anthropogenic origin.
The highly significant correlation of the metalloporphyrin content
with chlorophyll a indicates either that these
metalloporphyrins are formed in the water column or
that phytoplankton contribute to metalloporphyrin transfer from
water to sediments.
 Back to IO PAS Home Page
Back to IO PAS Home Page